In this article, we will review the tools that you can use within PPM Express to prioritize Roadmap items.
PPM Expres provides several powerful prioritization frameworks that will be helpful if you need to determine priorities for your Projects, tasks, objectives, ideas, and product features within your backlog.
Prioritizing Roadmap items
Items prioritization can help you understand which items should be moved from the Backlog to the Planned group in the first place. Prioritization of Roadmap items is available for both Roadmap groups: Backlog and Planned. When added to the Planned group, you can decide which items are more important and should be completed first.
Prioritization frameworks are presented as default views on the table view of the Roadmap dashboard. It is also possible to edit the default views or create your own ones. You can easily switch from one framework to another by changing the view.
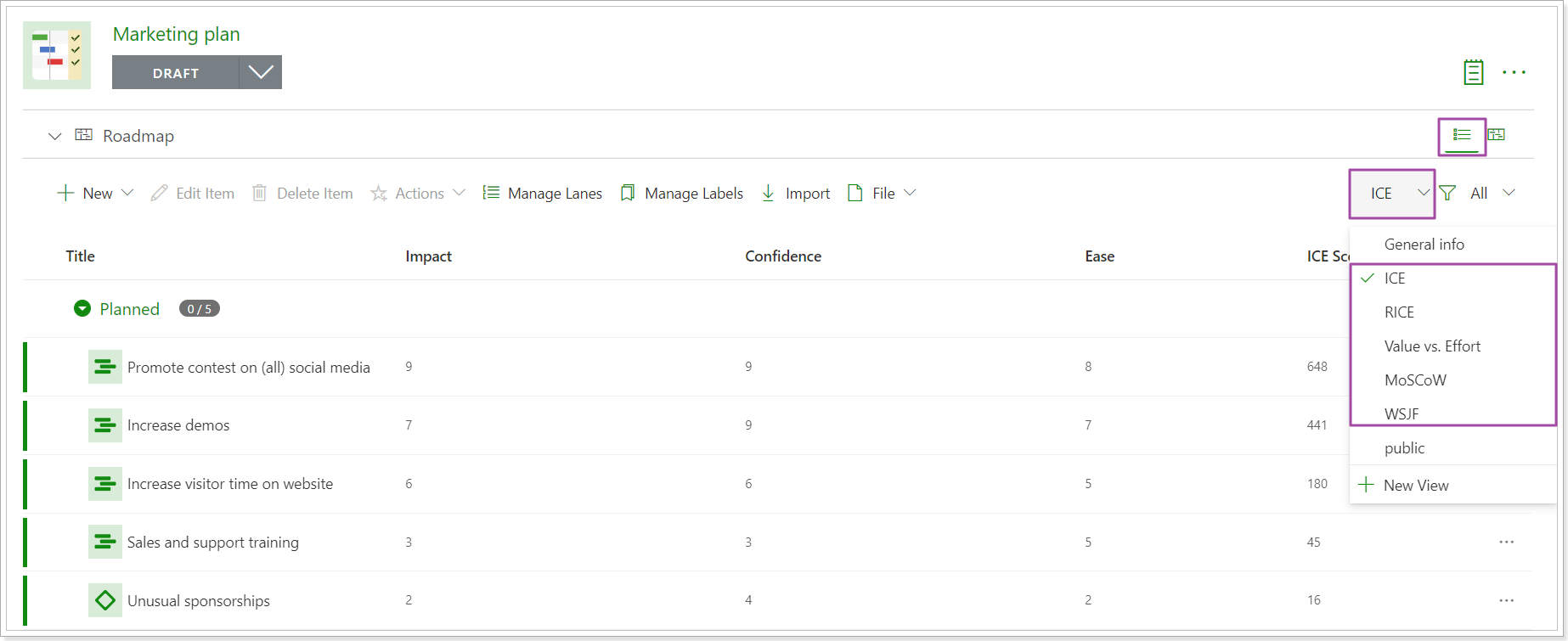
Each prioritization framework (view) has a set of fields where you can provide values as required. The total score for each item will be calculated automatically according to the formula of the selected framework.
To prioritize the Roadmap items perform the following:
1. Open the Roadmap dashboard and switch to the table view.
2. Click on the General info button to open the existing views and select one of the prioritization frameworks (ICE, RICE, Value vs. Effort, WSJF, MoSCoW). The ICE framework is selected as an example.
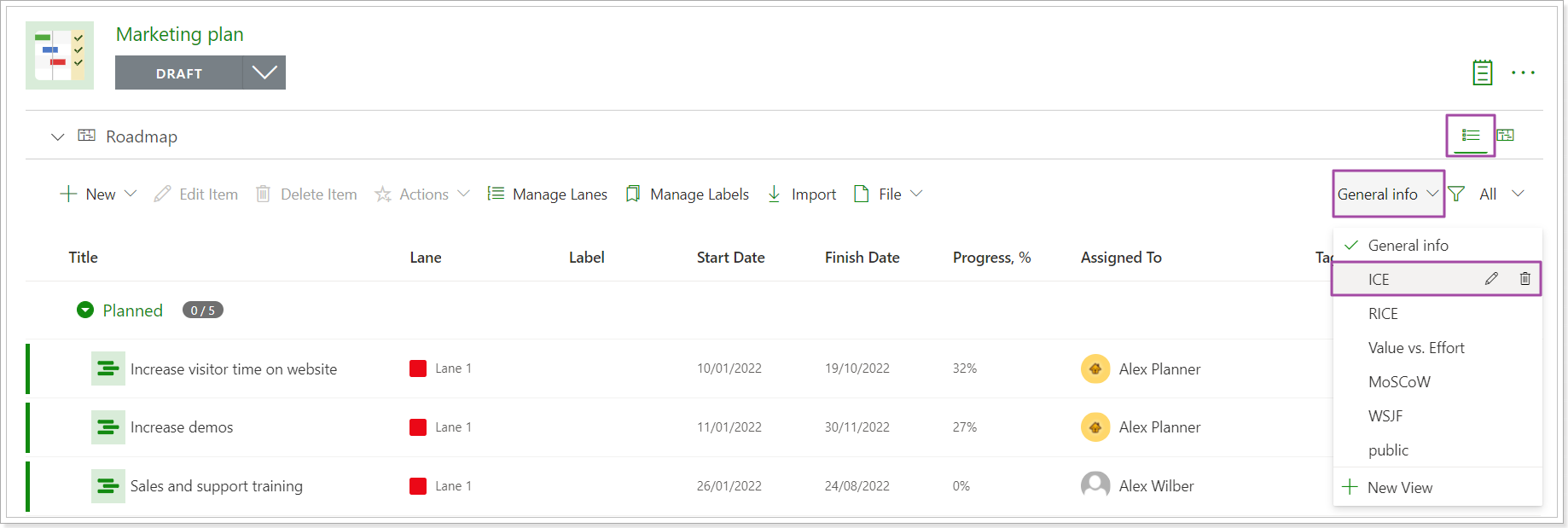
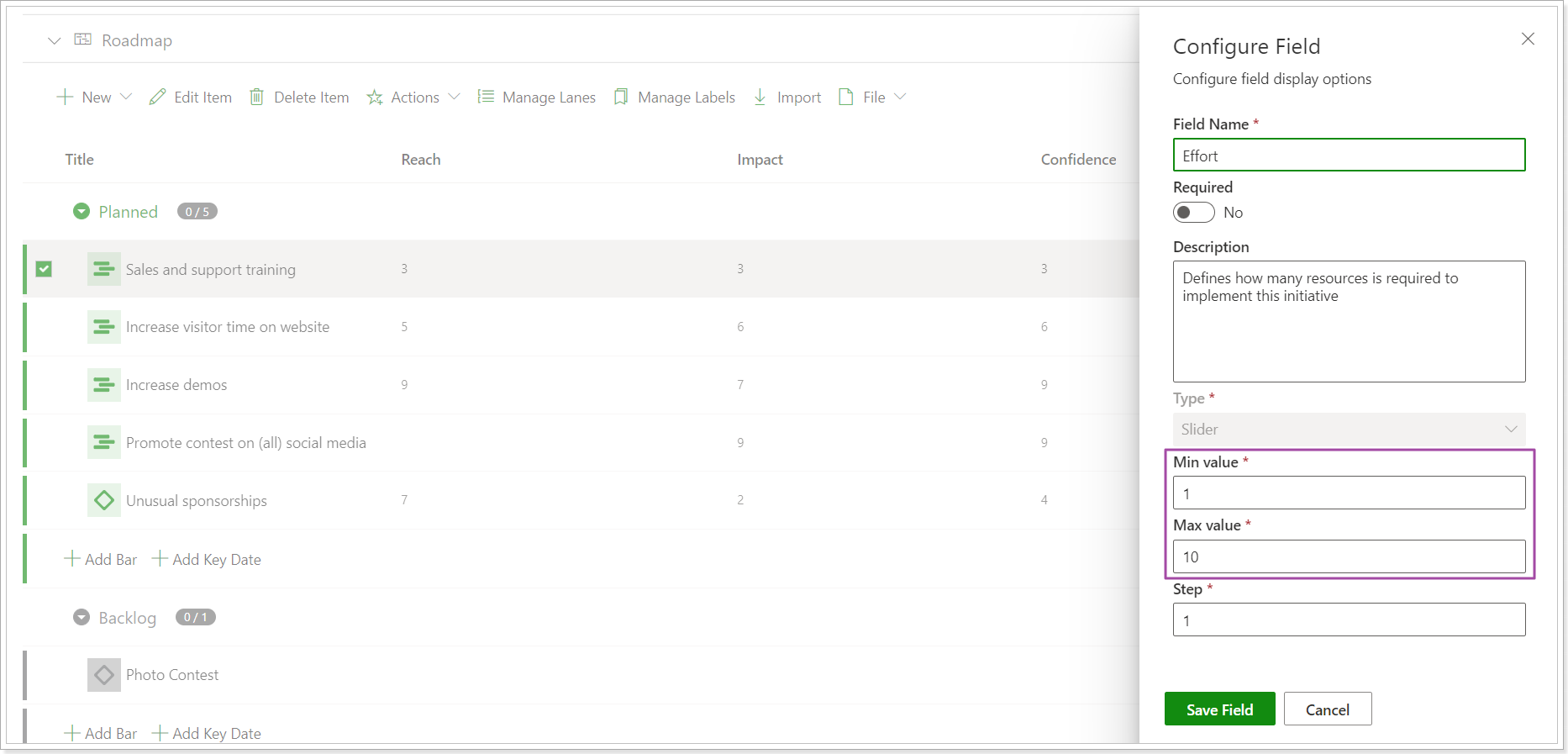
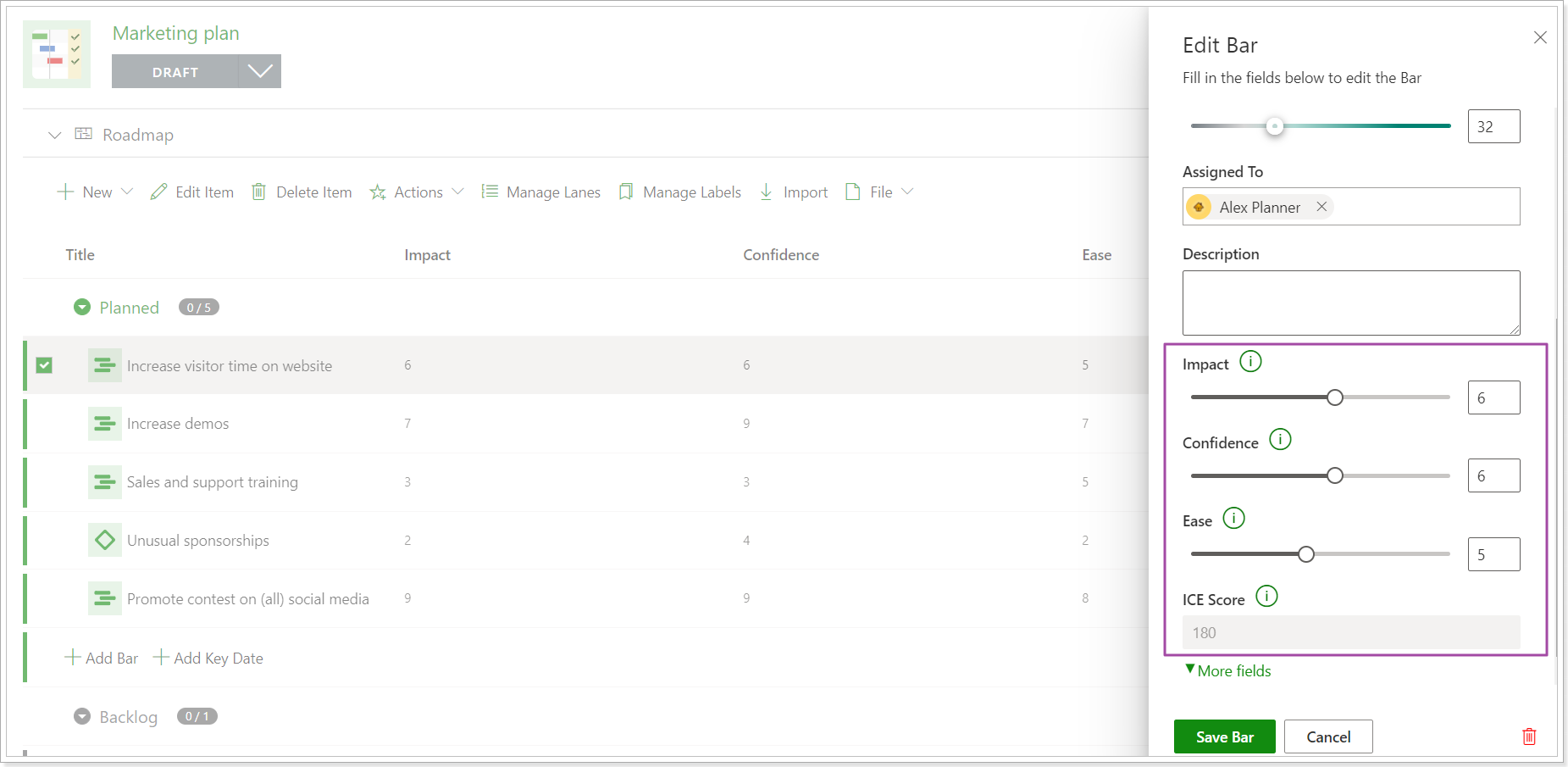
3. Click on the required item to open it for editing. The fields for the selected framework will be placed under the 'More fields' button and will be ready for editing.
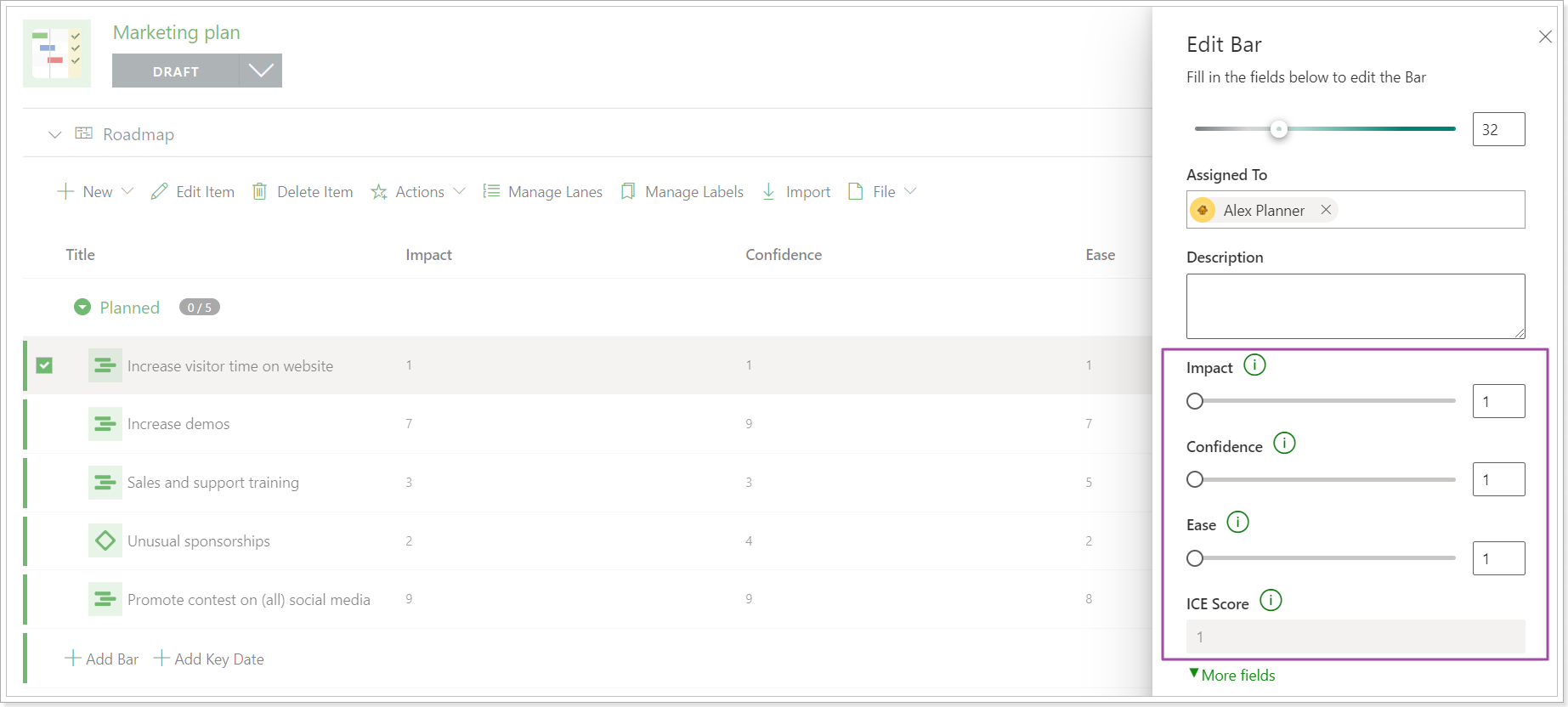
4. Set the values for each field as required. The Score field will be calculated at once.
Click the Save button.
5. The values will appear on the Roadmap table. When you add values for other items, you can sort the items by the framework score.
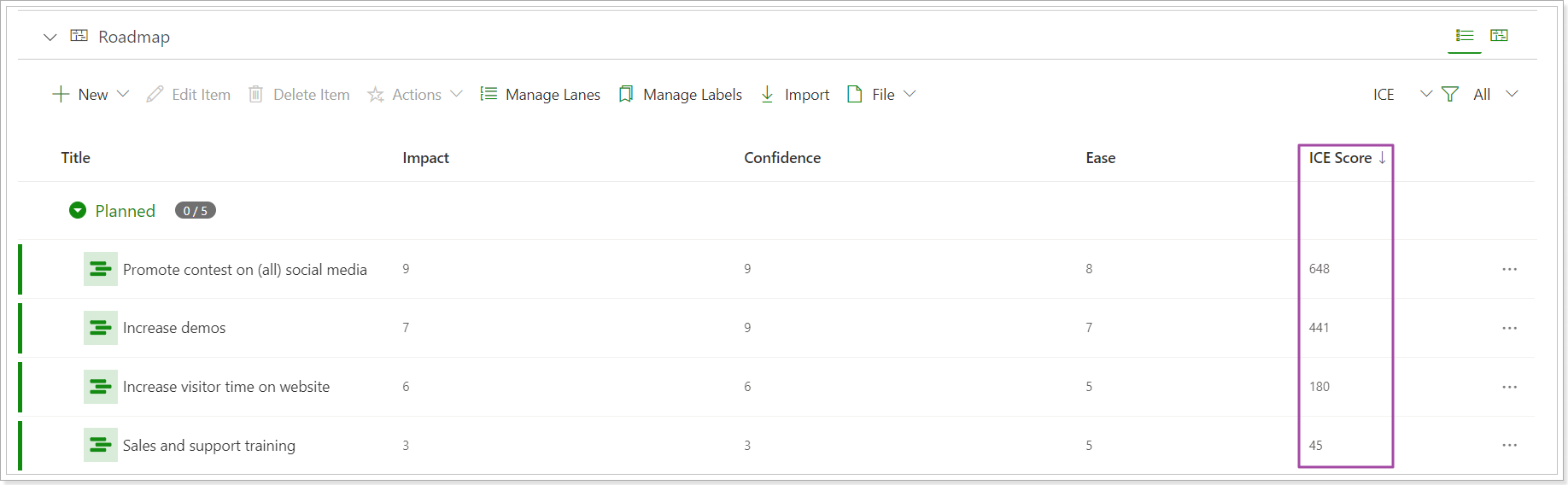
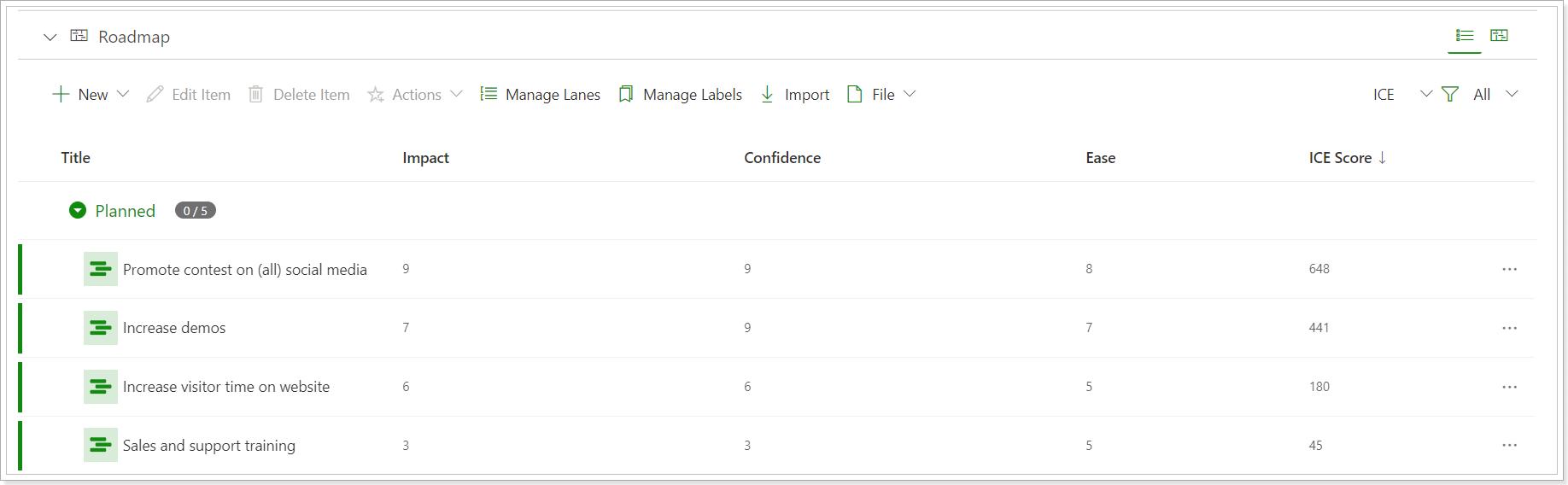
Prioritization frameworks score formulas
ICE Score: Impact*Confidence*Ease.
- Impact: Defines how much the initiative positively affects the key metric you are trying to improve.
Field Type: A slider from 1 to 10. - Confidence: Defines how confident you are that the impact would be realized.
Field Type: A slider from 1 to 10. - Ease: Defines how much effort and resources will be required to implement this initiative.
Field Type: A slider from 1 to 10.
This framework is great for teams that need to prioritize product features, user stories, or hypotheses. It considers both the value a feature will give and the efforts it will take, which is beneficial to the ROI.
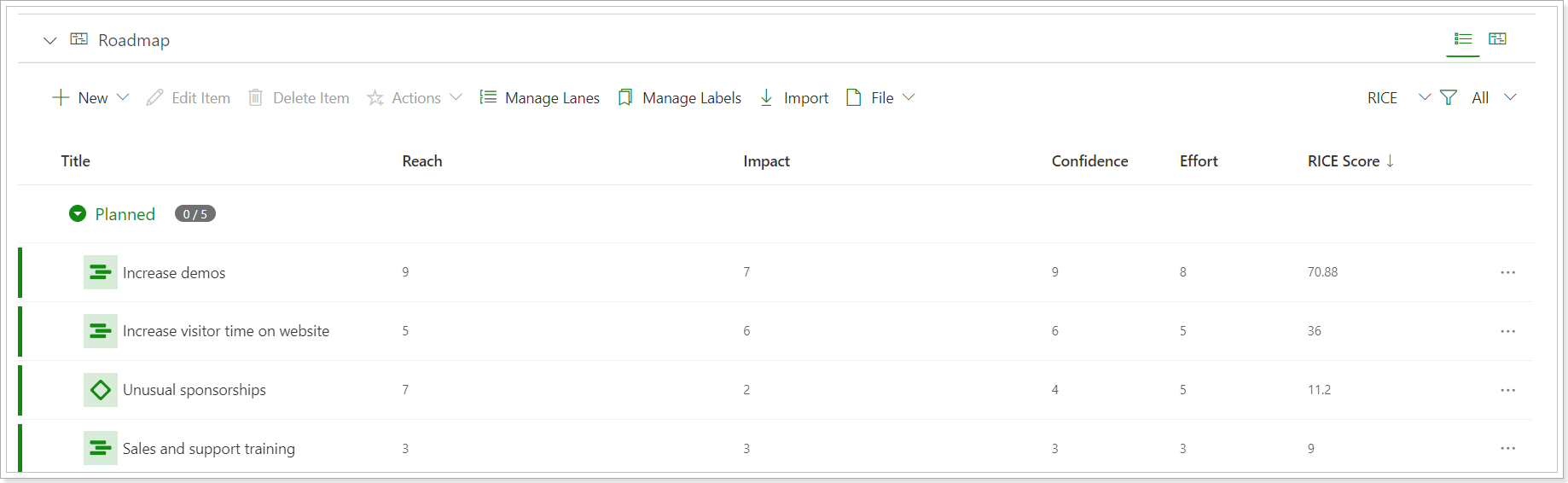
RICE Score: Reach*Impact*Confidence / Effort.
- Reach: An estimate of how many people this initiative will affect within a given timeframe.
Field Type: Integer. - Impact: Defines how much the initiative positively affects the key metric you are trying to improve.
Field Type: A slider from 1 to 10. - Confidence: Defines how confident you are that the impact would be realized.
Field Type: A slider from 1 to 10. - Effort: Defines how many resources are required to implement this initiative.
Field Type: A slider from 1 to 10.
Known as Intercom's internal scoring system for prioritizing ideas, RICE allows product teams to work on the initiatives that are most likely to impact any given goal.
After you provide values for each field, those individual numbers get turned into one overall score using a formula. This formula gives product teams a standardized number that can be applied across any type of initiative that needs to be added from the backlog to the Roadmap timeline view.
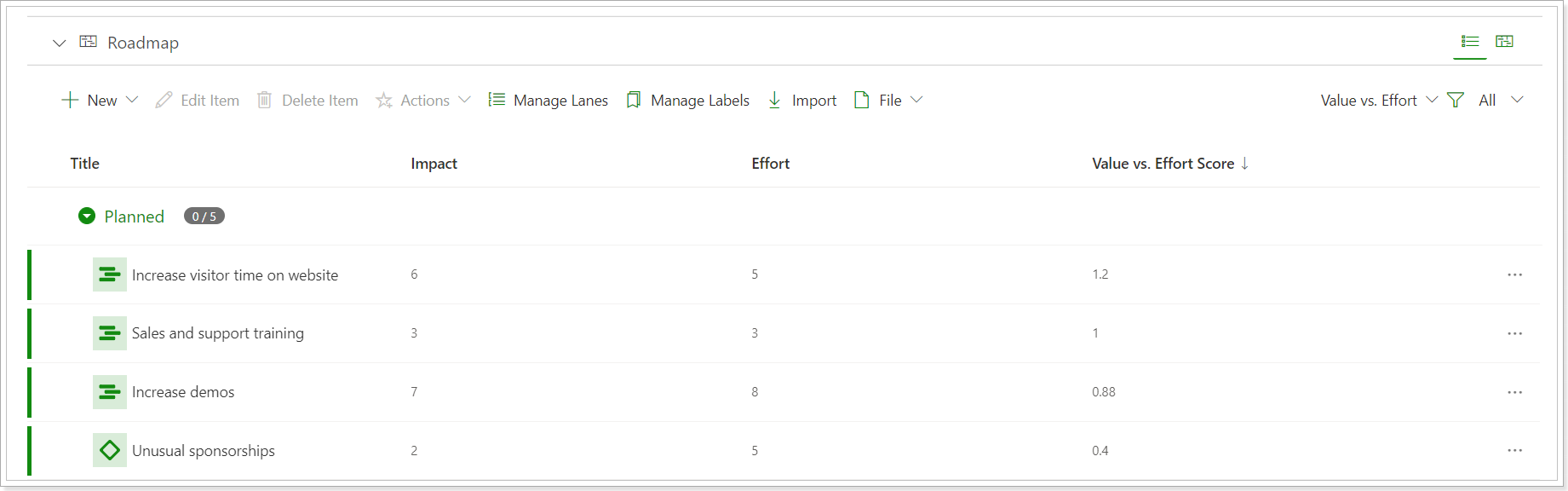
Value vs. Effort Score: Impact / Effort.
- Impact: Defines how much the initiative positively affects the key metric you are trying to improve.
Field Type: A slider from 1 to 10. - Effort: Defines how many resources are required to implement this initiative.
Field Type: A slider from 1 to 10.
This framework gives product teams a quick and easy way to visualize a set of quantified priorities.
This method of prioritization makes room for healthy discussions among stakeholders on what they believe value and effort means, which in turn helps product managers find the strategic alignment holes and fix them.
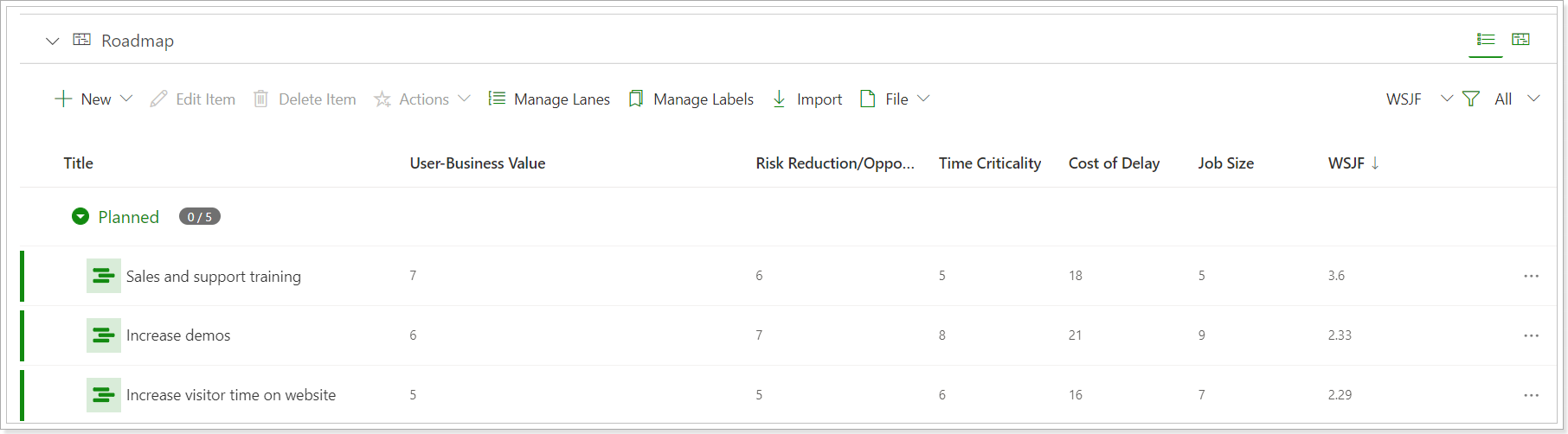
WSJF (Weighted Shortest Job First): Cost of Delay/ Job Size (a proxy for the duration).
Cost of Delay: User-Business Value + Time Criticality + Risk Reduction/ Opportunity Enablement. (Fields type: A slider from 1 to 10).
WSJF is a tool used in the Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe) to help teams prioritize a list of initiatives.
Any team in an organization can use the WSJF approach to sequence any initiatives. Marketing teams can use it to determine which Projects or campaigns will give the company the highest return on investment. Product teams can use it to decide which items to prioritize on the product backlog.
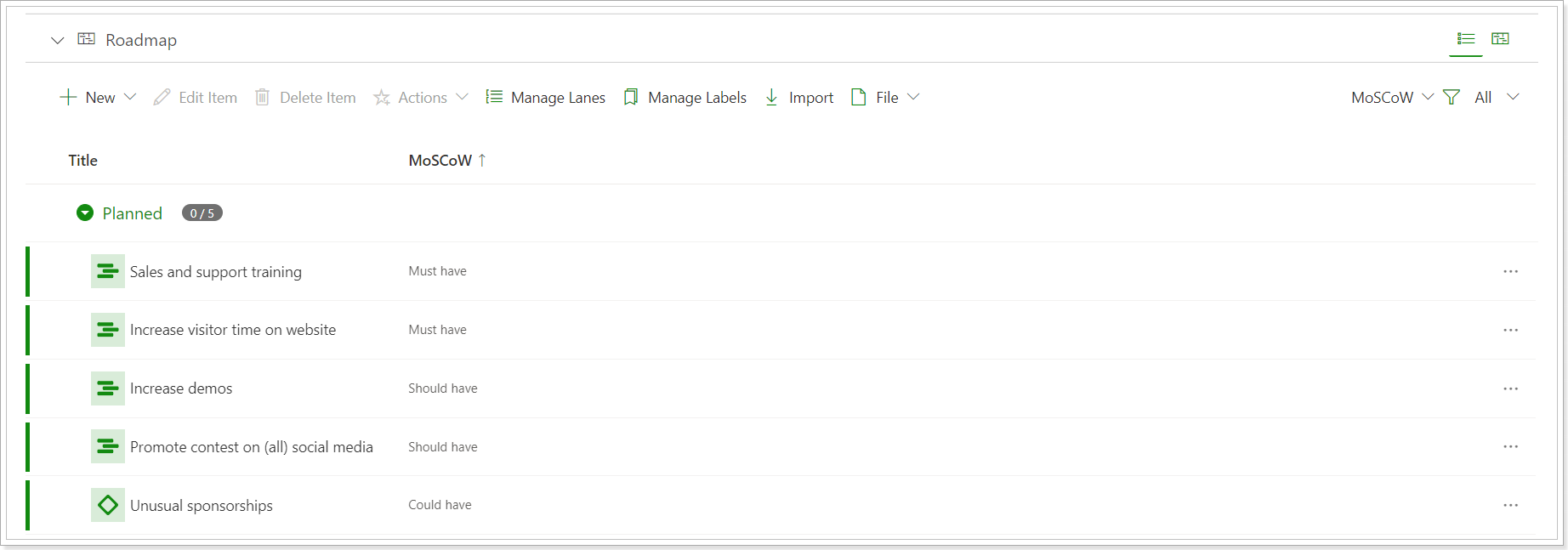
MoSCoW: The following values are available for selection instead of the formula:
- Must have: about mandatory items.
- Should have: the items great to have, but with not the highest priority.
- Could have: the essential small-scale improvements.
- Won't have: the items with the lowest importance.
The MoSCoW method allows you to figure out what matters the most to your stakeholders and customers by classifying features into four priority buckets.
This method is dynamic and allows room for evolving priorities. So a feature that was considered a “Won’t-Have” can one day become a must-have depending on the type of product.
The field values, e.g. from 1 to 10, can be customized by editing the required field (select view from the list => edit view => edit the required field).